Ukraine: An Election for the Oligarchs
Five years after the “EuroMaidan” protests in Kiev and elsewhere toppled the government of now-exiled former president Viktor Yanukovych, the people of Ukraine are set to elect a new leader. Over 34 million Ukrainian citizens will be eligible to cast their vote on 31 March, although several million will be prevented from participating due to the ongoing conflict situation in the country’s eastern Donbass region. Should none of the candidates receive an absolute majority, a second round of voting will be held on 21 April.
Ukraine consistently ranks among the poorest countries in Europe – last year it overtook Moldova to occupy the top spot in the list. The largest post-Soviet state after Russia in terms of population, it finds itself torn between the European Union promising economic integration and a limited degree of freedom of movement, and deepening the country’s relationship with Moscow, the largest consumer of Ukrainian exports to which Ukraine is tied by centuries of shared history, tradition, and repeated conflict.
EuroMaidan exacerbated the country’s ongoing economic decline and mounting social pressures in 2013–14, ultimately triggering the war in the Donbass region and the Russian annexation of the Crimean peninsula. These tensions have facilitated the rise of a vicious Ukrainian nationalism that the government led by current president Petro Poroshenko is not afraid to manipulate for its own purposes. Attacks on left-wing activists and ethnic minorities are becoming increasingly common, while armed far-right paramilitaries like the so-called “Azov Battalion” are normalized and integrated into mainstream political life.
That said, not everyone in Ukraine is happy about these developments. Although none of the candidates in the upcoming elections offer a particularly radical or progressive vision for the country, voters will at least be able to decide whether to endorse Poroshenko’s current course or throw their support behind another figure. Loren Balhorn of the Rosa-Luxemburg-Stiftung spoke with Kiev-based sociologist Volodymyr Ishchenko to get a better understanding of the candidates, the state of the county, and what is at stake for the people of Ukraine in 2019.
Loren Balhorn (LB): Ukraine is scheduled to hold presidential elections at the end of the month, preceding elections to the national parliament, or “Verkhovna Rada,” later this year. Is there anything special about the timing? What exactly is the president’s role in the Ukrainian political system, and what implications will the vote have for parliamentary elections in October?
 Volodymyr Ishchenko (VI): The timing is simple: it’s been five years since 2014 and the Maidan Uprising, when snap elections were called that saw Viktor Yanukovych and his Party of Regions lose a lot of strength. The first round of the presidential elections is at the end of the month, and it is very likely that there will be a second round because no candidate will receive over 50 per cent (at least according to polls).
Volodymyr Ishchenko (VI): The timing is simple: it’s been five years since 2014 and the Maidan Uprising, when snap elections were called that saw Viktor Yanukovych and his Party of Regions lose a lot of strength. The first round of the presidential elections is at the end of the month, and it is very likely that there will be a second round because no candidate will receive over 50 per cent (at least according to polls).
The president is very important in Ukrainian politics. The country is formally a parliamentary-presidential system, neither fully parliamentary nor fully presidential, but this is a very uneasy balance of power. The prime minister is an important position elected by the parliamentary majority, but the president also has influence over important government ministers. As is true of many post-Soviet states, however, beyond this formal institutional division of powers the informal divisions are much more decisive. Who is loyal to whom and who is dependent on whom plays a much bigger role in “real” Ukrainian politics than formal powers and privileges.
Petro Poroshenko, the current president, is the most important person in Ukrainian politics. His powers are formally limited but he has other ways to exercise influence and his own party, the “Petro Poroshenko Bloc” that forms the government together with the “People’s Front,” the party of former Prime Minister Arseniy Yatsenyuk. Another important figure in that party is the current Minister of Internal Affairs, Arsen Avakov, who is also a very wealthy man.
LB: Avakov also cultivates ties to the Azov Battalion, no?
VI: This is widely suspected, but the precise nature of those ties has never been proven. I am sceptical of the idea that the Azov Battalion is merely a puppet of Avakov, I suspect it is something like a mutually beneficial cooperation.
If Poroshenko loses we will see a lot of defections by MPs from his bloc. Ukrainian politics operates as what political scientists call a “neopatrimonial regime,” meaning it is characterized by rival, informal power blocs. If the Poroshenko Bloc loses, it will reshuffle loyalties in the parliament from one patriarch to another.
LB: What do you mean by “neopatrimonial regime”?
VI: By that I mean Ukrainian politics is characterized by competition between various power blocs, you could also call them pyramids or even clans. Poroshenko builds his pyramid while Arakov builds his own pyramid, etc. The current Prime Minister, Volodymyr Groysman, was originally perceived as a loyalist of Poroshenko, but now even he seems to be cultivating his own pyramid and will probably triangulate between various political blocs.
LB: How did Groysman come to replace Yatsenyuk?
VI: As friction between Poroshenko and Yatsenyuk grew, Poroshenko financed a public campaign against him, attacking him and calling for his resignation. But Yatsenyuk had a lot of support from the West, especially the U.S. Vice-President at the time, Joe Biden. Eventually an agreement was reached that he would step down and be replaced by Groysman.
This represented a conflict between different patrimonial structures within the governing elite, but also reflected a wider conflict between Ukrainian oligarchs and the West more generally. Many leftists in Ukraine see the country as a colony of the United States, but it’s much more complicated than that. Ukraine is definitely dependent on Western economic and financial aid, political support against Russia, etc., but it’s not a colony – it’s not ruled from the American Embassy. Local oligarchs like Poroshenko and Arakov have their own interests that they defend staunchly against the West. At its core, this is a conflict between transnational capital and the local bourgeoisie.
One key issue in these debates, and the crucial issue for the West and the IMF, was corruption and the establishment of “anti-corruption” institutions to ensure transparent rules of the game in Ukraine. But what they call “corruption” is basically the most important advantage that the Ukrainian bourgeoisie has against transnational capital: namely, their property is secure from the state while that of their competitors is not. This is also what scares away potential international investors. Because of this fear, foreign direct investment (FDI) is actually declining despite the Ukrainian government’s steps toward Western integration.
LB: So fear of corruption is harming investment?
VI: Yes, although the war is of course another factor.
In the beginning, in 2014 and 2015, we had a lot of people in the government without Ukrainian citizenship who received their positions because they were neoliberal, Western-oriented professionals, like the Lithuanian citizen Aivaras Abromavičius who was a minister under Yatsenyuk. Gradually, those neoliberal reformers were pushed out and replaced by people loyal to the ruling oligarchs. Yatsenyuk being replaced by Groysman was just one particularly important example of this process.
LB: It sounds like a pretty grim scenario. But even if electoral politics is just competition between oligarchic factions, certainly there must be some other issues being debated at least on the surface? What are the dominant themes the candidates are using to attract support?
VI: Poroshenko has been most successful in setting the agenda with an aggressively nationalist campaign – his main slogan is “Army, Faith, Language.” He side-lined the socially populist issues that Yulia Tymoshenko tried to raise by portraying the election as a choice between him or Putin and depicting his opponents as puppets of Moscow.
LB: And is it working?
VI: Yes, to some extent. His support has been rising in the polls since the recognition of the independent Ukrainian Orthodox Church by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople.
LB: Was that split between the Ukrainian Church and Moscow supported by the government?
VI: Yes, it was actively organized by Poroshenko as a strategy to win the election. Formally, the Ukrainian Orthodox church enjoyed broad autonomy but was dependent on the Moscow Patriarchate and was recognized by other Orthodox churches. A separate church founded in the early 1990s, the Kiev Patriarchate, was unrecognized by any other international church but still fairly popular in the country. In reality most people didn’t care which church they attended. The split was purely political, there were no theological differences.
Poroshenko started to push the theme in 2017 and 2018 that the Ukrainian Orthodox Church was something like an “agent of Moscow” in Ukraine. The details are quite complicated, and to be honest many people in Ukraine didn’t really understand these structures until last year either, but for people who care about national issues, who care about Ukraine asserting itself against Russia, this was an important step. Nevertheless, it looks like the majority of local parishes will actually stay with the Moscow Patriarchate.
LB: You have alluded to the conflict with Russia several times now as setting the terms of the debate, and making it easier for politicians to distract from social questions by focusing on nationalism. Is there any kind of visible, vaguely progressive social opposition in the country?
VI: Most politicians and the three leading candidates for the president are not significantly different on the question of the conflict in the Donbass region. Poroshenko, Tymoshenko, and Volodymyr Zelensky are all within the patriotic consensus, although Poroshenko is more militant. Candidates who actually have a different opinion and are not as popular sprang from the former Party of Regions, later branded the “Opposition Bloc.” They failed to negotiate a common candidate for the so-called “Southeast,” the region where the Russian-speaking minority mostly lives. Despite raising important issues like peace in Donbass, re-claiming national sovereignty from the West, and re-industrialization, these candidates – Yuriy Boyko and Oleksandr Vilkul – are representatives of major oligarchic financial-industrial groups. There is no significant “grassroots” movement behind the issues. There are of course labour struggles, and there have been some strikes, but they are weak. There are some feminist mobilizations but they are miniscule compared to the radical nationalists. Not just the anti-capitalist “Left,” but also progressive liberalism is very weak.
The Left is in a bad situation. The Communist Party has been banned. They are appealing the ban but their public visibility has declined to practically zero. Their leader, Petro Symonenko, tried to register as a presidential candidate but was not accepted by the government, and no other relevant left-wing parties exist on the national level.
LB: Government corruption, oligarchic control of the economy, a decimated Left – a lot of this sounds familiar. Couldn’t we, at least to some extent, compare conditions in Ukraine to the situation in all of the former Eastern Bloc countries?
VI: I don’t think so. EU membership makes a big difference, it imposes certain rules that are absent in Ukraine. The presence of strong oligarchs, for example, is pretty specific. The other Eastern Bloc countries don’t have a strong local bourgeoisie, but are largely dominated by Western capital. There are no Polish oligarchs, Czech oligarchs, Hungarian oligarchs – we only hear about Russian and Ukrainian oligarchs. What makes Ukraine different is that the oligarchic system is pluralistic. We have multiple, competing oligarchs, whereas in Russia and Belarus one neopatrimonial pyramid managed to emerge as dominant in the last 15 years.
The promise of EU membership restructured Eastern European politics beginning in the 1990s, whereas this was never a prospect in Ukraine, Russia, or Belarus. But we still didn’t see the rise of any figure like Vladimir Putin or an Alexander Lukashenko in Ukraine. I think this has to do with the country’s divided identity: almost every election has been framed as a question of “East vs. West,” with one candidate supported by the western half and the other by the eastern half. In this sense it’s comparable with Donald Trump: any time a Ukrainian president comes to power he is opposed by half the population from day one. This makes it very difficult to consolidate nationwide power.
LB: Are there not also economic aspects to the East/West division?
VI: Yes, the East has more heavy, Soviet-era industry, exporting primarily to the markets of the former USSR and uncompetitive on Western markets. For example, the people supporting Yanukovych and opposing EuroMaidan were at least partially concerned about keeping their jobs in a Ukrainian economy dominated by the EU.
LB: So it’s not only a nationalist issue, but also one of bread-and-butter economic issues?
VI: Yes, absolutely.
LB: Speaking of “East vs. West,” has anything changed since Ukraine’s accession to the visa-free regime for Schengen states in 2017?
VI: That was one of very few positive developments under Poroshenko, and he’s touting it a lot during the campaign. Freedom of movement is of course something good and something we support, but it was particularly good for younger, highly educated Ukrainians in the major cities.
It has also facilitated increased labour migration, which has really risen since 2014. I don’t have any precise statistics but we’re talking about millions of people. Many Ukrainians go to work in Poland, which actively recruits them because they are seen as culturally and linguistically “closer” to Poles (unlike refugees from the Middle East). You could say that cheap Ukrainian labour is subsidizing the Polish economic boom. The Czech Republic is also popular, and Germany will probably be next.
As workers from the eastern EU states like Bulgaria and Poland move west to work they’re replaced by cheaper labour from Ukraine, but no one moves to Ukraine. There is a lot of discussion in the Ukrainian media about how it simply does not make sense to work in the country when you can make two or three times more across the border.
LB: But does this not mean that the Ukrainian labour market is gradually getting tighter? Wouldn’t it at least theoretically put organized labour in a more advantageous position to fight for higher wages?
VI: Yes, theoretically! But Ukrainian trade unions are very weak, and they have failed to take advantage of the situation.
LB: You recently gave an interview to Jacobin Magazine in which you compared the situation of the Ukrainian Left with that of Latin America in the 1970s. I found that very striking, given that the Left was quite large in Latin America at the time and microscopic in Ukraine today. Could you flesh out that comparison a bit? Where exactly do you see similarities?
VI: Ukraine is a deindustrializing, peripheral economy. Most Soviet-era industry fell apart after 1991, and what remains is not competitive on the Western European market. Ukraine has thus become a supplier of raw materials with low added value like iron. In this sense it is a very peripheral capitalism characterized by extreme inequality and powerful oligarchs, like Latin America. There is also the major role played by far-right paramilitaries – this doesn’t happen anywhere else in Europe, except for briefly in former Yugoslavia. We also have a strongly pro-American and highly dependent government, very similar to Latin America.
I think it’s logical to look for comparisons and lessons from similar historical social formations. If the Ukrainian Left is looking to fight a corrupt, authoritarian, anti-Communist regime, and given how weak the Left and even liberalism is, we have to work together to fight for basic democratic rights and against the nationalist hysteria to lay the base for a movement that could perhaps become more significant in the future. Here I see parallels to the Latin American Left’s struggle against dictatorship in the 1970s and 1980s.
LB: Do you think it’s possible in a geopolitical situation where tensions between the EU and Russia are so prominent to formulate a broad, democratic programme that stands above this fray?
VI: It’s obviously very difficult, but what other options do we have? Become puppets in the geopolitical game? There was a split on the Left in 2014 when many chose EuroMaidan and the “West” while others chose Anti-Maidan and the “Russian” side. Both sides ended up tailing more powerful right-wing forces and failed to formulate their own independent positions.
LB: But would anything else have been possible?
VI: Well, obviously we can’t seriously entertain the building of a strong left-wing party under such difficult conditions. What is possible, however, is to maintain some kind of milieu for left-wing ideas. The groups and networks that exist have to consolidate a possible embryo for a strong Left in the future. It’s important to be realistic and understand what’s possible or completely impossible. We might not be able to formulate some kind of “Third Camp” in Ukrainian politics right now, but that is our objective situation, and we should try to figure out what we can realistically do. We should work on strengthening our groups, our unions, our intellectual initiatives, to hopefully be able to do something bigger in the future.
Corbyn, Podemos, and Mélenchon are inspiring figures, but we need to understand what is specific about the political regime in our country and respond in a specific way. We need to try to expand the range of the possible for left politics at the moment. Even if it isn’t so inspiring and very weak, we still have to try. The kind of system that exists in Ukraine can’t last forever. There are many contradictions, divisions, and cleavages exacerbated by the ruling groups, and all of these will lead to a situation at some point where weaker groups might become politically relevant and important again.
LB: Before we wrap up I wanted to ask you about the third major candidate, Volodymyr Zelensky. If I understand correctly, he stars in a TV show about a politician and has now become the politician he plays on TV. Is that correct – and is he popular? Does he have a chance at winning or is this a stunt?
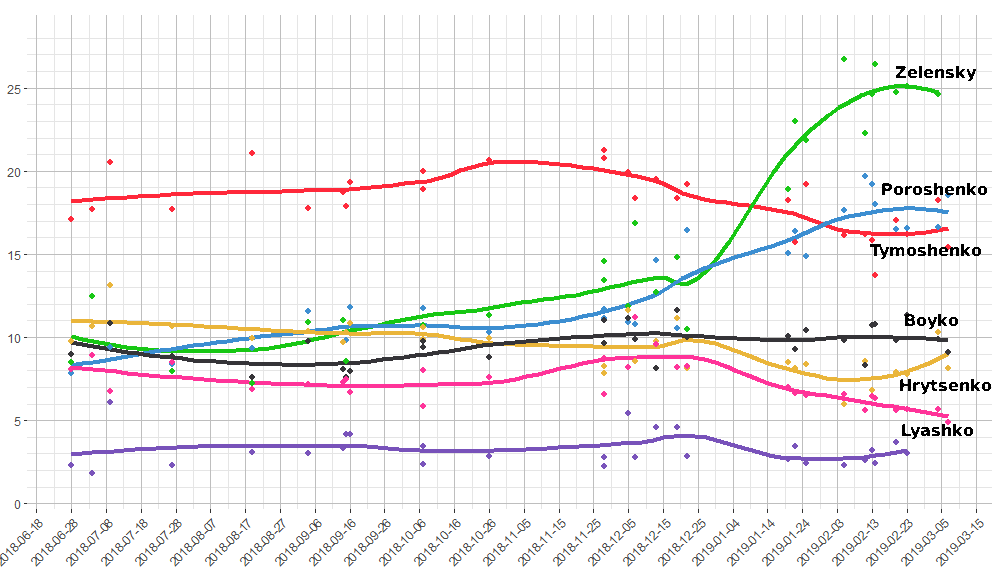
VI: Actually, he’s currently the most popular politician in the country. According to polls he has significantly more support than both Poroshenko and Tymoshenko, and could very possibly become the president.
There are basically three groups of people voting for him: firstly, fans of his TV show, a very popular comedy about Ukrainian politics. Another large group are just so disappointed and tired of these oligarchs that they will vote for any fresh face.
LB: So he’s similar to Donald Trump in some ways?
VI: In some ways, but what’s different from Trump is the third group of his supporters, namely people who are voting for him because he is perceived as less nationalist than the other candidates. Zelensky himself is Russian-speaking, he’s from the central Ukrainian city of Kryvyi Rih, and has attracted lots of support from Russian-speaking citizens.
That makes Zelensky different from Trump – he’s actually trying to campaign on unifying themes, not divisive ones. He opposes Poroshenko’s attempts to push the Ukrainian language on Russian speakers, for example.
Another thing that makes him different from Trump or Beppe Grillo is that he has no populist movement behind him, or any movement at all for that matter. All he has is his TV show, around which he is now trying to build a political party from scratch. This is different from other populist figures – there was no mass mobilization preceding him. Trump, for example, is obviously somehow a result of the Tea Party movement, while Grillo represents the Five Stars Movement (in Italy).
Another difference is his connection to Igor Kolomoisky, one of Ukraine’s richest oligarchs now in opposition to Poroshenko who founded the country’s largest bank, Privat Bank, and still owns a controlling share of the national airline. Zelensky’s show is broadcast on one of Kolomoisky’s eight TV stations, and one of his lawyers is a key architect of Zelensky’s party, Sluha Narodu, which translates to “Servant of the People” (also the name of his show). Right now it’s not possible to say how independent Zelensky is. I wouldn’t call him a puppet, but there are definitely connections to the ruling class.
All of this means that Zelensky will be very weak if he wins, and not only because he’s inexperienced. For the first half year he won’t have much support in parliament. He has no loyal political party behind him. He will surely get some opportunists to defect from other parties, but hardly a majority. I don’t know what he could do in that situation. After the parliamentary elections he might face a more favourable constellation, but it will also depend on how he does in the first months.
It’s impossible to say how he would perform as president. He has zero political experience. I fear that he may understand politics even less than Donald Trump. He is a blank page on which anything can be written.
LB: So he reflects the vacuum in civil society more generally?
VI: Exactly. He is a glaring symptom of what’s going on in Ukrainian society. People hate the oligarchs, they hate the faces they’ve seen for decades. Revolutions come and go, elections come and go, but life just gets worse and worse. People don’t want another five years of Tymoshenko or Poroshenko and are happy to vote for any recognizable fresh face who isn’t implicated in serious corruption. People are voting less out of hope than out of anger. Better to vote for an incompetent comedian than the same old corrupt experts.
At the same time, civil society is so weak that it couldn’t put up any competing figure. Only a TV star was able to do that, nobody from the pro-Western, liberal NGOs came even close. None of those figures poll even one per cent. This says a lot about Ukrainian “civil society”: it’s totally incapable of producing competent, popular leaders.
If he is elected, it will be strong proof that the people are sick of the old style of politics, that they aren’t being manipulated by Poroshenko’s nationalism and want something better. Nevertheless, I am very sceptical that Zelensky will be able to change anything. Real change in Ukraine will be a much longer process, and will require the building of a different kind of political opposition that we haven’t seen in this country for a very long time. •
This article first published on the Rosalux.de website.