Remembering Pierre Beaudet: Teacher, Internationalist, Comrade
Pierre Beaudet, Presente!
Pierre Beaudet, a Quebec leader in international solidarity and progressive scholarship, died in Montréal on the night of March 7-8. Pierre was for decades a central organizer, author and editor in a range of grassroots movements and left publications. His presence and inspiration will be sorely missed by many, both young and old, as Judy Rebick indicates in this tribute she published in rabble.ca, an online magazine she co-founded two decades ago.
We publish an article by Pierre, written less than a week before he died, that addresses the very issue Judy cited as one that she would look to him to explain. Pierre wrote it in his capacity as director of Alternatives, the international solidarity organization he founded and to which he had recently returned. My translation. And I conclude by briefly recalling some of my own memories of Pierre as a friend and comrade. — Richard Fidler

The War in Ukraine
This text is intended to introduce a debate within Alternatives. It argues that this conflict will change everything, including in our area of solidarity and international cooperation. As in any important debate, there are theories, strategic issues, choices to make in our practice. This text does not answer everything. It expresses a view that is not the only approach now being expressed. It will therefore be necessary to have a lengthy and in-depth discussion in the coming period, and this contribution will have achieved its objectives if it can simply break the ice. — PB
Ukraine, with a population of 43 million, is foundering in the war unleashed by Russia’s invasion. There are thousands of victims. A large part of the country’s infrastructure, including energy and communications facilities, has been destroyed. In the streets of Kyiv and the other major cities, the Ukrainian people are engaged in street battles with the powerful Russian army. Hundreds of thousands of Ukrainians have fled into exile.
Meanwhile, the United States and its allies are imposing severe sanctions against Russia while organizing major military assistance but without willing to become involved on the terrain. There does not appear to be any possibility of negotiation, at least in the short term. The conflicts will likely increase, with further destruction.
The Aggression
Russia prepared its attack over a long period. It was launched last week with the hawkish speech by President Vladimir Putin, who denied the very reality of Ukraine as the sovereign state and territory of a people with the right of self-determination. In the initial days, the Russian army destroyed with its short and long range missiles a major part of the military infrastructure as well as crucial energy and communications systems. Russia claimed it would spare civilians, which would exclude massive indiscriminate bombing. The Russian advances have continued, encountering as they reached the cities a strong Ukrainian resistance. In military terms, this resistance relies on small decentralized contingents with very effective weapons such as mobile anti-air and anti-tank missiles. It is also getting unlimited support in weapons and money from the United States and its allies.
If the war becomes bogged down in the cities, it will result in destructive combat in the midst of highly-populated regions. The collateral costs will be huge, and this may lead the United States and NATO to become more involved. That is what Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky is hoping, and in this he no doubt reflects the majority opinion that resistance to the aggression is the only outcome on offer. Russia, however, cannot easily back down, as this would be a terrible defeat for Vladimir Putin. So there is a great risk that the war will go on.
How Did We Get to This Point?
The implosion of the Soviet Union in 1989 profoundly destabilized what was then the second biggest power in the world. The vast majority of the republics that were part of the USSR broke free, including Ukraine which became independent in 1991.
Coming into office in the early 2000s, Vladimir Putin promised to be the “strong man” who would re-establish that power. First he focused on annihilating the Chechen rebellion. He turned then to what he defined as the “near exterior” including Georgia, Belarus and some republics in central Asia, combining threats and interventions with cooptation of local elites. This was relatively effective, and gave Putin the idea that he could expand his interventions, for example by supporting the regime of Bashar El-Assad in Syria, where he gambled on the weakening and failure of the US strategy. The “strong man” then followed this up with various measures to paralyze the opposition in Russia. Putin’s approach borrowed from the tradition of the USSR under Stalin in imposing a centralizing and repressive state along with attempts to carve out a place in the global arena.
Role of the United States
Since the demise of the Soviet Union thirty years ago, Russia has continued to be confronted by Washington, beginning with the latter’s reneging on the promise made to Gorbachev, the last Soviet president, that it would not incorporate the former components and allies of the USSR into NATO. Instead, the US has built a veritable iron circle with several of these territories, threatening Russia indirectly. There were some limits to this strategy, so the United States launched the terrible “endless war” in the Middle East and Central Asia, as well as its incursion in the Balkans. But its failure after some years resulted in opening up areas of conflict in which Moscow was able to insert itself, in Syria, as mentioned, and with Iran and other countries anxious to avoid the destruction experienced by Iraq. Little by little, Russia could see its horizon broaden by looking to China and other “emerging” countries aspiring to greater autonomy within the global system. The Russia-China convergence is of course a product of the explicit US strategy that seeks to prevent China from moving into the lead in capitalist globalization.
A Fight to the Finish
This gave Putin the impression that he could strike a major blow in Ukraine. When a staunchly anti-Russia government was imposed in 2014, Russia reacted by annexing the Sebastopol region and supporting the pro-Russia territories in eastern Ukraine. A “mini war” (with 14,000 victims, nonetheless) prepared the way for the present conflict. Demanding that the United States exclude any possibility of Ukraine membership in NATO, Putin was well aware that this issue was non-negotiable. Some European states (including Germany and France) had a more accommodating position, but lacked the ability to say explicitly what could have been an alternative project: acceptance of a sovereign Ukraine with neutral status (as were Finland and Austria in the past), establishing of a new European agreement involving disarmament of borders, Russia’s integration in the agreements, intra-European economies, etc. In the end, as Putin had expected, the US view prevailed.
Leap Into the Unknown
Now that Russia has attacked, there is no turning back. Either Putin wins his bet by the subjugation of Ukraine, which would allow him to “entrust” to a new government the job of “re-establishing order.” Or the situation will drag on into an endless conflict – unless Russia decides to wage war in the cities even if it means destroying them, with their people, as was done in Syria. In either case, the conditions will have been created to revive a new kind of cold war, fueled by fierce attacks on the Russian economy, increasing militarization of central Europe, the Baltic states and Poland, support to the Ukrainian resistance, etc.
This new Cold War 2.0 will represent an immense realignment of priorities and strategies. NATO, its relevance diminished in recent years, will return in force. The member states will be required to increase substantially their military spending and become directly involved in the strategy of counter-attacking and weakening Russia: harsh economic sanctions, military and political support of states and movements confronting Russia, a major “battle of ideas” to reinvent the monster that had created such fear in Western opinion for more than 30 years. And so on.
Consequences for Canada
No doubt the Canadian government will follow the US line, as it has done since the beginning of the conflict. With the immense polar frontier between Canada and Russia, this could have major consequences. Canadians’ reluctance to invest the billions needed for purchasing weapons of mass destruction will be seriously weakened, with a resulting surge in the military budget financed by severe cutbacks in other budget allocations. And Canada, eager to increase its oil and gas exports via huge pipeline projects to the Pacific and Atlantic, will be able to relaunch these projects on the pretext that they are part of the “war effort” against Russia. We will have to pay close attention to what is going to happen with the proposed LNG project designed to bring Alberta’s gas through Quebec.
This Canadian shift will of course be strongly encouraged by pursuit of the war, which, we repeat, was initiated by Russia. Public opinion in Canada, and not only among Canadians of Ukrainian descent (1.8 million persons) has understandably mobilized against Russia.
On Solidarity and International Cooperation
The area in which we are involved will be strongly affected. It is certain that humanitarian aid is going to be oriented toward the millions of Ukrainians who are in or on the way to exile. That is necessary, from a humanitarian standpoint. What is not is its discriminatory nature. There are at this point at least 10 million Syrians, Iraqis, and Afghans (to mention only those) languishing in detention camps administered by states in the pay of NATO member countries. The great majority of these wretched of the earth know already that they will never be accepted as refugees. Meanwhile, some disregarded conflicts are breaking out in the Horn of Africa while the international (dis)order prevents the UN from seriously intervening.
No one should be surprised, therefore, if the humanitarian aid (administered by Foreign Affairs Canada) is not sharply reorganized to assist Ukraine – which is not dishonorable but will become so if the already very modest resources offered to other countries and peoples in crisis are reduced.
In the coming period, the new board of directors of Alternatives, with other NGOs and international solidarity movements, will have to look at how we can promote our views and act responsibly in the eyes of a population that is currently distressed by the conflict and its possible consequences.
Among the options now being discussed in our circles, we will have to develop ourselves our basis of action taking into account past experience and the uncertainties in the present context.
- Peace must be re-established as soon as possible, if only in the form of a ceasefire that gives those responsible some time in which to extricate themselves from the present impasse.
- This peace process should include the United Nations. While the European Union and NATO are major protagonists, they cannot be left to tackle this.
- We act in solidarity with the Ukrainian resistance that aims to re-establish an inclusive and peaceful sovereignty without abuses of national minorities. Our solidarity can be exercised in the area of humanitarian assistance wherever in the country people are suffering the impact of the war.
- Humanitarian aid, and development assistance to poor countries (especially in Africa) must not be reduced to meet Ukraine’s needs.
- Canada must not align its policies with those of the United States, via NATO or otherwise. It should promote disarmament and the peaceful resolution of conflicts while defending human rights without discrimination.
Russia invaded Ukraine four days ago in blatant violation of the UN Charter and international law. The United States and their NATO allies, including Canada, have plunged us as well increasingly into this war by a flurry of sanctions and outrageous statements. •
A True Friend and Comrade…
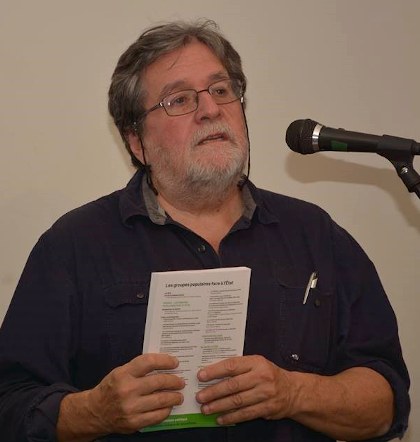

Although I was long acquainted with his work I did not meet Pierre Beaudet until the World Social Forum in Caracas in 2006. We soon became good friends. Soon afterwards, Pierre found employment at the University of Ottawa, where he was instrumental in establishing the School of International Development and Global Studies. He invited me to participate in his efforts to establish an Ottawa section of the Collectif d’analyse politique (CAP), publishers of the Nouveaux Cahiers du socialisme, a semiannual review Pierre had co-founded in 2009. On three occasions he included me as a guest lecturer in his course on Latin American social movements and politics.
When teaching at UOttawa, and later the Université du Québec campus across the river in Gatineau, Pierre, who commuted from his home in Montréal, usually stayed overnight for a day or two per week at my home. He always brought with him books and magazines – Le Monde Diplomatique and the New York Review of Books were among his favourites – to leave with me and we often exchanged Marxist books we both found useful. Conversations with Pierre were a delight; he was knowledgeable and insightful on a vast range of subjects, and I enjoyed his ironic sense of humour.
My niece Nancy Burrows, who has known Pierre longer than I through her active leadership in the Quebec women’s movement (she coauthored a chapter in one of his books on L’Altermondialisme), mentioned to Pierre in an email exchange that she had heard he knew her uncle. His response captured our friendship rather nicely, I think:
“I spend two nights a week with your uncle, with whom I very much enjoy discussing late into the night why the Indonesian Communist party screwed up in 1966, or if Lenin had listened to the mutineers at Kronstadt, and other similar stories that have remained in the head of the unrepentant Marxist oldtimers like us. It has helped me endure Ottawa more easily… We also discuss intersectionality in the Dogon country in Mali, the place of LGBTQs in the present Chilean movement, peaceful insurrections that get things moving more than petitions. What would have happened if Rosa Luxemburg had not been assassinated, etc., etc., it never ends between us.”1•

This article first published on the Life On The Left website.
Endnotes
- “Je passe deux soirées par semaine avec ton oncle avec qui j’ai bien du plaisir à discuter tard dans la nuit sur pourquoi le Parti communiste indonésien s’est planté en 1966, ou encore si Lénine avait écouté les mutins de Kronstad, et d’autres histoires du genre qui sont restés dans la tête des pépés marxistes non repentis dans notre genre. Cela me fait endurer plus facilement Ottawa… Nous discutons aussi de l’intersectionnalité dans le pays dogon du Mali, de la place des LBGTQ dans le mouvement chilien actuel, des insurrections pacifiques qui font bouger les choses plus que les pétitions. Sur ce qui serait arrivé si Rosa Luxemburg n’avait pas été assassinée, etc. etc. ça n’arrête jamais entre nous…”